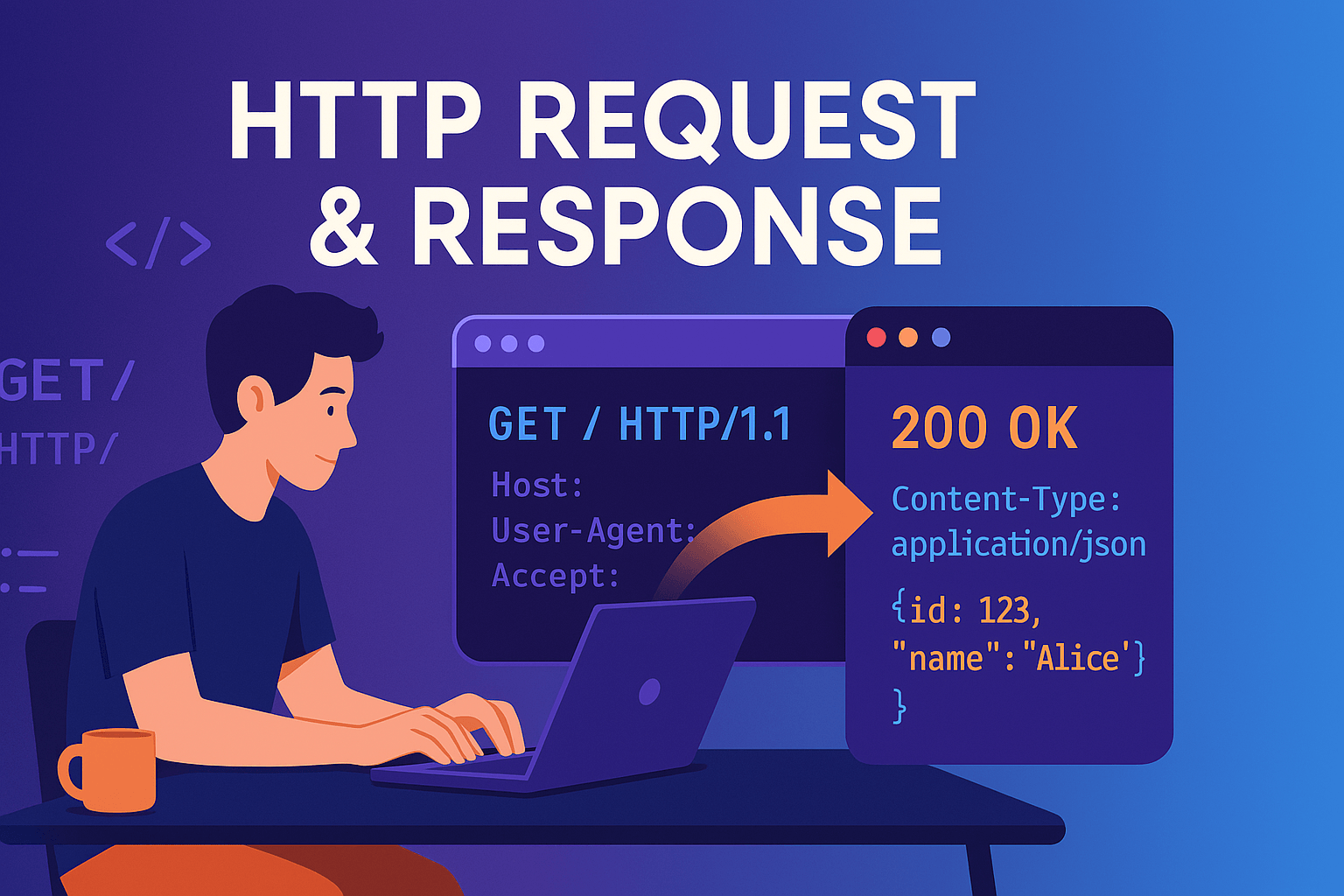
HTTP Request
A message sent by the client to request data from the server or to ask it to perform a certain operation.
Three Parts of the HTTP Request Structure
Request Line
This is the first and mandatory part of the request. It consists of three main components:
- Method – (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
- Request URL/Path – (e.g.,
/api/users/123?q=http&page=2) - HTTP Version – (
HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2)
Headers
Additional information — i.e., metadata — is sent here. Metadata is in key-value form and provides extra details about the request.
Most commonly used HTTP headers:
HostUser-AgentAcceptContent-TypeContent-LengthAuthorizationCookie
Real case example:
Message Body / Payload
After the headers, a blank line is left and the body is provided if present. It is mainly used in requests that send data to the server, such as POST, PUT, PATCH.
The body is written in the format specified by the Content-Type header, e.g., application/json.
General HTTP Request Format:
HTTP Response
The response returned to an incoming HTTP request from the client. Its purpose is to:
- Indicate the outcome of the request (successful? error? redirection?)
- If successful, return the requested result/data to the client
Three Parts of the HTTP Response Structure
Status Line
The first and mandatory part of the response. It consists of three parts:
- HTTP Version – (
HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2) - Status Code – A three-digit code returned by the server.
- Reason Phrase – A human-readable description of the status (e.g.,
OK,Not Found,Internal Server Error)
Status Code Categories:
| Category | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1xx | Informational – The operation is in progress |
| 2xx | Success – The request was successfully processed |
| 3xx | Redirection – A redirection is required |
| 4xx | Client Error – An error on the client side |
| 5xx | Server Error – An error occurred on the server |
Headers
Additional information (metadata) sent by the server to the client, also in key-value format.
Most commonly used response headers:
Content-Type– Type of the returned data (application/json,text/html, etc.)Content-Length– Length of the body (in bytes)Set-Cookie– To send a cookie to the clientCache-Control– Caching directives for the responseDate– The date when the response was sentServer– Technical information about the serverLocation– Provides the new URL for redirection (with 301, 302)
Real case example:
Message Body / Payload
If the server returns data as a response, that data is provided in the body.
📌 Only some status codes (200, 201, etc.) include a body.
For example, in statuses like
204 No Contentand304 Not Modified, there is no body.